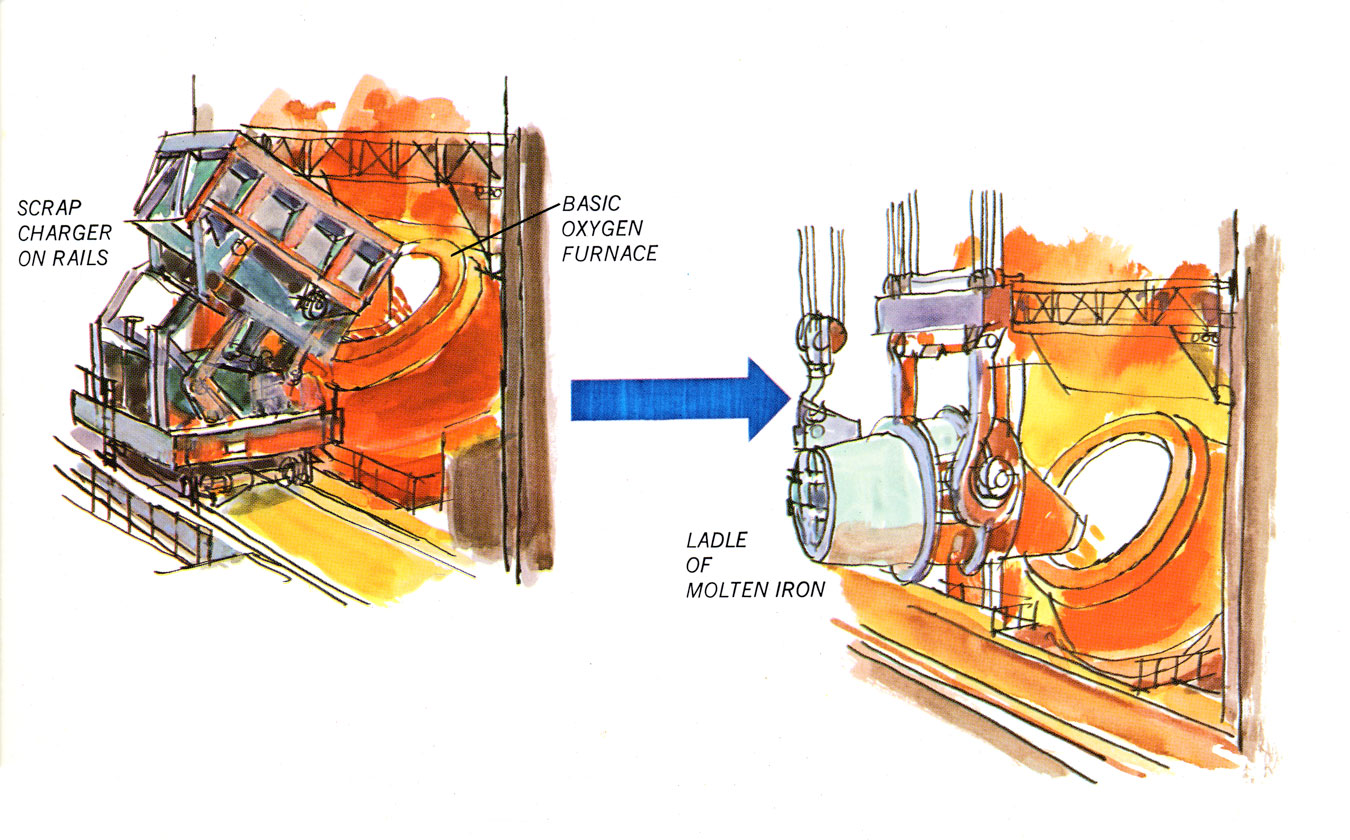
A basic oxygen furnace, called a BOF, is a pear-shaped steel vessel with refractory lining and an open top. The charge consists of about 75% molten iron and 25% scrap steel.
Steel is produced in an basic oxygen furnace by the following steps:
1. The charge is dumped into the furnace.
2. An oxygen lance (pipe) is lowered and pure oxygen blows into the furnace at high pressure.
3. The oxygen reacts with the carbon and impurities that are in the molten iron.
4. When the carbon reaches the desired amount (up to 0.9%) the process is finished.
This is a low-cost process, as it does not use electricity or fuel, and makes steel quickly (in about 45 minutes), but it does not allow full control over the chemical composition of the steel.
